

Tooth erosion is a dental condition in which the enamel covering the teeth deteriorates due to prolonged acid exposure. This erosion differs from tooth decay, which involves bacterial activity. Enamel acts as the primary protective barrier, and as it erodes, the underlying dentin is revealed.
This exposure increases the teeth’s sensitivity to external factors, often causing sharp pain or discomfort. Tooth erosion is often irreversible since enamel cannot regenerate once lost. Therefore, early diagnosis and preventive care are essential to avoid serious dental complications.
In severe cases of tooth erosion, the dentin exposure can make the teeth appear yellow and increase the risk of fractures. Moreover, the condition is progressive, meaning that if not addressed promptly, the damage can worsen over time, impacting both oral health and aesthetics.
The frequent consumption of acidic foods and beverages plays a significant role in tooth erosion, as repeated acid exposure wears down the enamel over time.
Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are packed with citric acid, which can weaken enamel if consumed frequently or in large amounts.
Soft drinks, energy drinks, and flavored sparkling water contain high levels of carbonic and phosphoric acids, both of which erode enamel with prolonged exposure.
Wine, particularly white wine, is highly acidic, and regular consumption can lead to the gradual breakdown of enamel, especially if combined with poor oral hygiene.
Acid reflux, a condition associated with GERD, causes stomach acids to travel up into the mouth, leading to tooth erosion over time. Continuous acid exposure from reflux not only affects the enamel but can also contribute to other oral health issues, such as increased sensitivity and bad breath.
Saliva serves as the body’s natural defense against tooth erosion by neutralizing acids and washing away food particles. A decrease in saliva production, known as xerostomia, makes the mouth more vulnerable to acid attacks and prevents the natural remineralization of enamel, thereby accelerating the erosion process.
Saliva serves as the body’s natural defense against tooth erosion by neutralizing acids and washing away food particles. A decrease in saliva production, known as xerostomia, makes the mouth more vulnerable to acid attacks and prevents the natural remineralization of enamel, thereby accelerating the erosion process.
Swimmers who spend extended periods in chlorinated pools are at risk of tooth erosion if the pool water’s pH is not properly balanced. When pH levels drop too low, the acidic water can erode the enamel on teeth, particularly if individuals spend several hours swimming regularly without rinsing their mouths afterward.
Certain medications, including aspirin, antihistamines, and some antidepressants, can lower saliva production or increase the acidity of the mouth, contributing to tooth erosion when taken frequently. Long-term use of such drugs without proper oral care can result in significant enamel wear, as the mouth remains more acidic for longer periods.
You can contact us here to learn more about Cosmetic Dentistry, Dental Crown, Dental Implant and General Dentistry to make an appointment and to get information about our services.
Identifying the early signs of tooth erosion is crucial to halt its progression and safeguard overall oral health. One common symptom is increased sensitivity, which occurs as the enamel thins and exposes the underlying dentin. This sensitivity often causes discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sugary foods and drinks, making everyday eating and drinking more challenging.
Another noticeable symptom is discoloration. As enamel erodes, the yellowish dentin layer underneath becomes visible, giving the teeth a dull or yellowed appearance. This can affect the brightness of the smile and may make teeth appear less healthy, impacting both aesthetics and self-confidence. In more advanced stages, cracks, chips, and changes in tooth shape become evident.
The teeth may develop smoother or rounded edges, and front teeth can appear translucent at the tips due to the thinning enamel. Weakened enamel also makes the teeth more prone to cracks or chips, while affected areas may appear unusually shiny or glossy, signaling significant enamel loss. Without intervention, these symptoms can progress, leading to severe issues like cavities, infections, and even tooth fractures.

During the early phase, the enamel begins to thin, causing slight sensitivity when consuming hot or cold foods.
As enamel erosion progresses, teeth can become increasingly sensitive, and the likelihood of discoloration rises significantly.
In advanced cases of tooth enamel erosion, the enamel wears away entirely, exposing the dentin. This leads to heightened sensitivity and a greater likelihood of cracks or chips forming.
Since enamel cannot regenerate, taking steps to prevent further tooth erosion is crucial. Frequent dental visits and changes in lifestyle can help slow down the advancement of this condition.
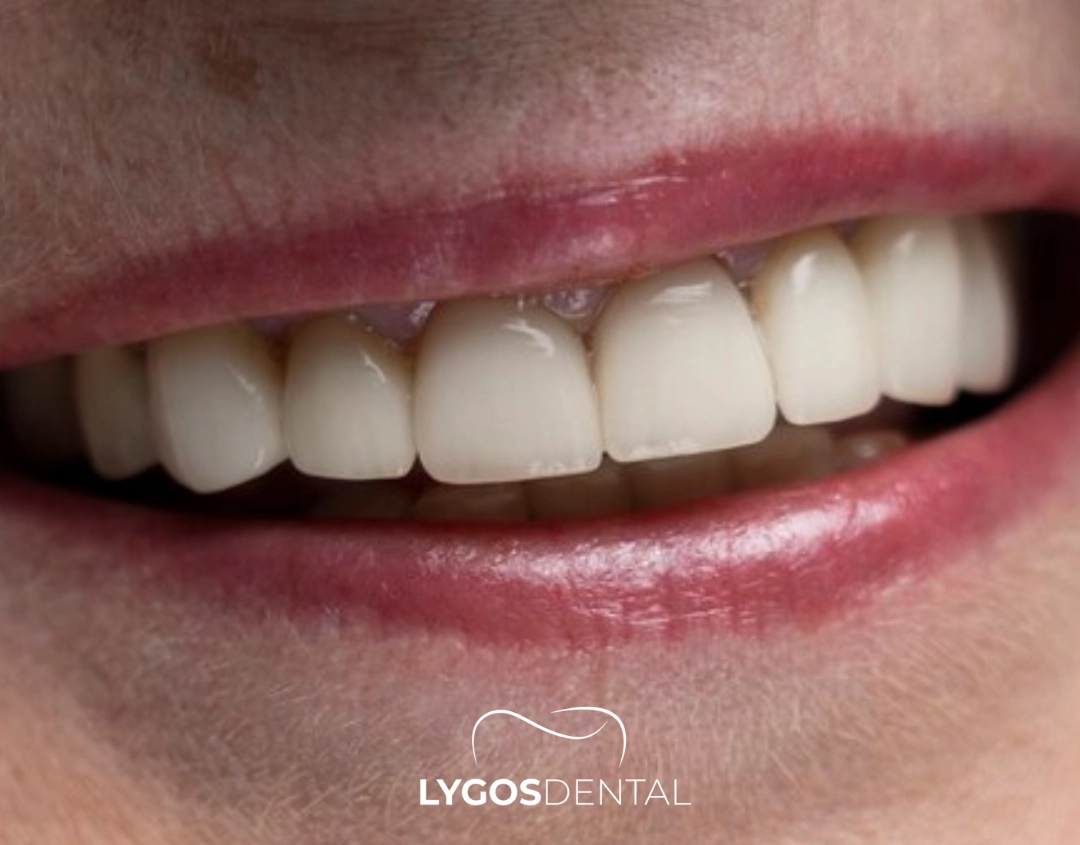
The erosion of enamel on teeth compromises the natural barrier that protects the inner structures of the tooth. When enamel erodes, teeth become more vulnerable to damage, leading to functional and aesthetic concerns. While fluoride treatments and dental bonding can offer some protection, preventing tooth erosion is the most effective strategy.
The most critical aspect of managing tooth erosion is understanding how daily habits impact oral health. Brushing your teeth right after consuming acidic foods can actually worsen enamel erosion. This practice can spread the acids across the tooth surface, leading to further damage to the enamel. Instead, rinsing with water and waiting at least 30 minutes before brushing helps protect the enamel from further erosion.
One of the most impactful steps you can take to prevent tooth erosion is to cut back on acidic foods and drinks. Items like citrus fruits, sodas, and certain fruit juices can elevate acid levels in the mouth, leading to enamel degradation. Instead, choose less erosive options such as water or milk, which can help wash away acids and promote a healthier environment for your teeth.
After enjoying acidic foods or beverages, it’s wise to hold off on brushing your teeth for at least 30 minutes. Immediate brushing can exacerbate damage to softened enamel. Allowing saliva time to neutralize the acids and re-harden the enamel before brushing will provide better protection for your teeth.
Brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush or exerting excessive pressure can accelerate the wear of enamel. Switching to a soft-bristled toothbrush can effectively clean your teeth while being gentle enough to help preserve enamel integrity.
Fluoride is a vital mineral that strengthens tooth enamel and offers crucial protection against tooth erosion. Incorporating fluoride toothpaste into your routine and considering professional fluoride treatments can significantly bolster your teeth's resistance to decay and erosion.
Maintaining proper hydration is essential for rinsing away harmful acids throughout the day. Staying well-hydrated by drinking ample water helps rinse your mouth while also encouraging a healthy flow of saliva. Furthermore, chewing sugar-free gum can enhance saliva production, acting as a natural barrier against acidity and aiding in the neutralization of harmful substances in your mouth
Scheduling routine dental visits is vital for the early identification of tooth erosion and other oral health issues. During these examinations, your dentist can assess your dental condition and suggest tailored treatments to manage any developing concerns.
If tooth erosion has already caused noticeable damage, restorative procedures such as dental bonding, veneers, or crowns might be necessary. These treatments can restore both the functionality and appearance of your teeth while providing an additional layer of protection against further erosion. By adopting these preventive strategies and seeking professional dental advice when necessary, you can effectively shield your teeth from erosion, ensuring a vibrant and healthy smile for years to come.

Special Note:
Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate

Special Note: Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate
Selenium Retro, Ataköy 7-8-9-10. Kısım, D-100 Güney Yanyolu No:18/A, 34158 Bakırköy/İstanbul
© 2025, LYGOS DENTAL. All Rights Reserved.