
Teeth are not only important for aesthetics but also play a critical role in speech, chewing, and overall oral health. However, when teeth are lost for various reasons, this can negatively impact both physical and social life. So, how does tooth loss affect speech? In this article, we will examine in detail the effects of tooth loss on speech, potential consequences, and treatment options.
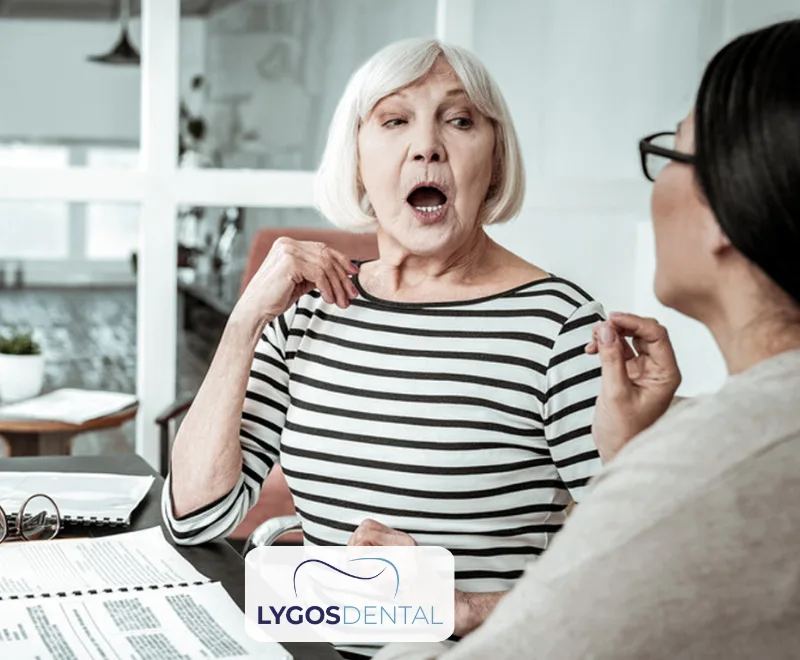

Teeth, especially the front teeth, play a vital role in correctly pronouncing certain sounds. For example, sounds like “s,” “t,” “f,” and “v” depend on the proper positioning of the teeth and tongue. When teeth are missing, pronouncing these sounds can become difficult, and words may be spoken incorrectly or be hard to understand.
When considering how tooth loss affects speech, factors such as the location, number of missing teeth, and duration of the loss must be taken into account. Missing front teeth typically lead to more noticeable speech problems, while missing molars primarily affect chewing.
Tooth loss does not only cause mispronunciation of sounds but can also affect the speed and fluency of speech. People with missing teeth may speak more slowly or hesitantly. This can make social communication challenging and reduce self-confidence.
Research shows that one of the most tangible examples of how tooth loss affects speech is a “lisp,” a distortion of the “s” sound. Additionally, some individuals may avoid speaking to hide their missing teeth, leading to communication difficulties and social isolation.
Tooth loss does not only affect speech; it can also alter the functioning of the tongue muscles and jaw structure. Missing teeth can disrupt the normal placement of the tongue, which may cause sounds to be produced incorrectly or incompletely.
It is important to emphasize that the impact of tooth loss on speech is not only aesthetic but functional. Especially in long-term tooth loss, permanent speech disorders can occur. Healthy and complete teeth help maintain proper breathing, sound production, and oral muscle balance.

Speech disorders not only affect word pronunciation but can also have serious social consequences. People may struggle to express themselves and feel hesitant to speak in public due to missing teeth.
This highlights that the question of how tooth loss affects speech also has social importance. Studies show that individuals with missing teeth often experience lower self-confidence and become more reserved in social relationships, which can affect both professional and personal life.
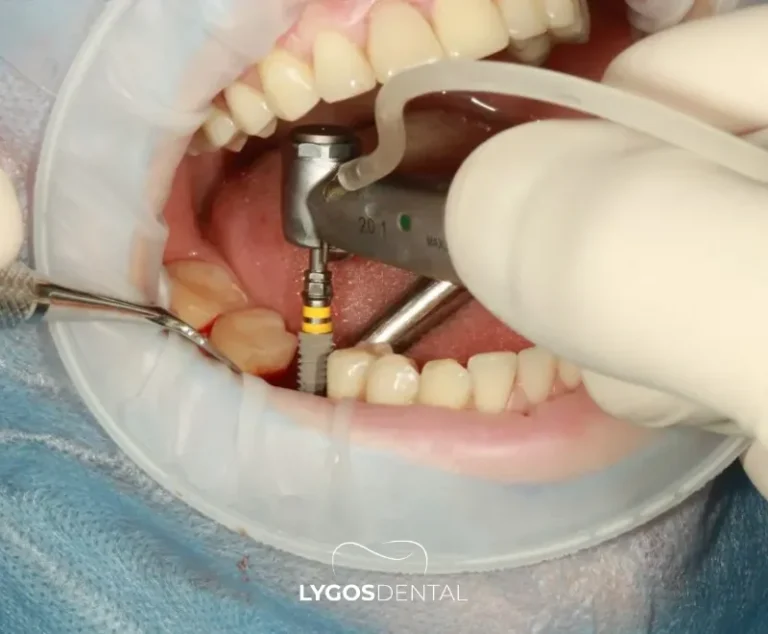
It is possible to reduce or completely eliminate the effects of tooth loss on speech. Today, several treatment options are available:
These treatments directly address how tooth loss affects speech and help individuals achieve a healthy oral structure both functionally and aesthetically.
While it is not always possible to completely prevent tooth loss, proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups can significantly reduce the risks. Tooth decay, gum disease, and trauma are the main causes of tooth loss.
Regular brushing, flossing, a balanced diet, and dental check-ups twice a year can minimize the negative effects of tooth loss on speech. Early intervention also makes it easier and more effective to replace missing teeth.
Oral health is directly linked to speech and social communication. Missing teeth can lead to speech disorders, loss of self-confidence, and difficulties in social interactions. However, modern dentistry offers many solutions that address how tooth loss affects speech. Early intervention and regular care can greatly reduce the impact of tooth loss on both speech and social life.
It should be remembered that healthy teeth are not only a beautiful smile but also the key to effective communication.
You can contact us here to learn more about Cosmetic Dentistry, Dental Crown, Dental Implant and General Dentistry to make an appointment and to get information about our services.
The impact of tooth loss on speech depends on the location and number of missing teeth. Missing front teeth usually cause noticeable speech problems quickly, while missing molars primarily affect chewing.
No, not all tooth loss affects speech in the same way. Front teeth directly impact speech, while some back teeth mainly affect chewing and overall oral health. However, long-term tooth loss can affect tongue and jaw muscles, potentially causing speech disorders.
Yes, dentures and bridges can replace missing teeth and significantly improve speech. Properly fitted dentures enhance both aesthetics and functional speech.
Dental implants provide a permanent and natural solution for missing teeth. In most cases, speech disorders are completely corrected, allowing the person to pronounce words comfortably.

Special Note:
Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate

Special Note: Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate
Selenium Retro, Ataköy 7-8-9-10. Kısım, D-100 Güney Yanyolu No:18/A, 34158 Bakırköy/İstanbul
© 2025, LYGOS DENTAL. All Rights Reserved.