Oral and dental health is an integral part of our overall well-being. However, many people are unaware of how serious gum diseases can be. Among these conditions, one of the most common and progressive is chronic periodontitis. This condition progresses silently and, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss and systemic health problems. So, what exactly is chronic periodontitis? What are its symptoms, causes, and treatment methods? You’ll find the answers to all these questions in our article.
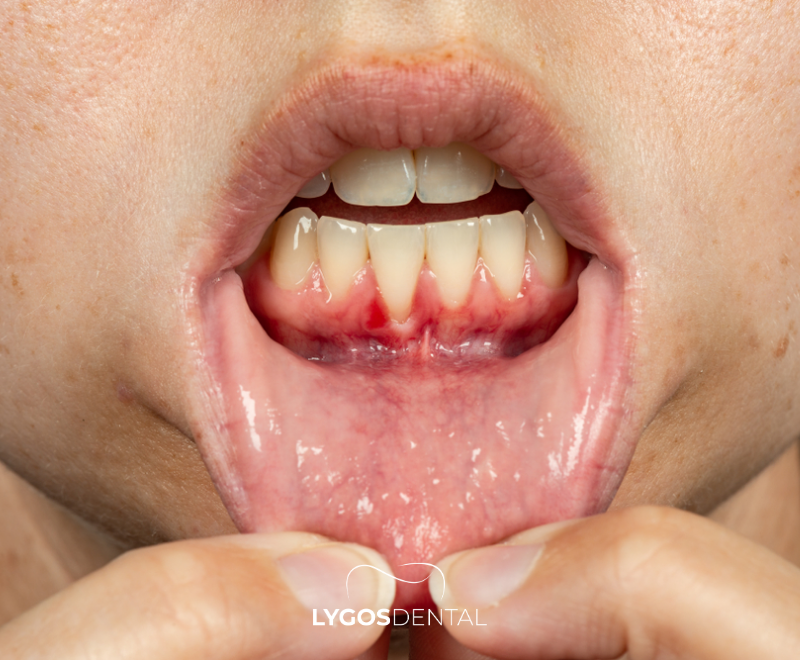
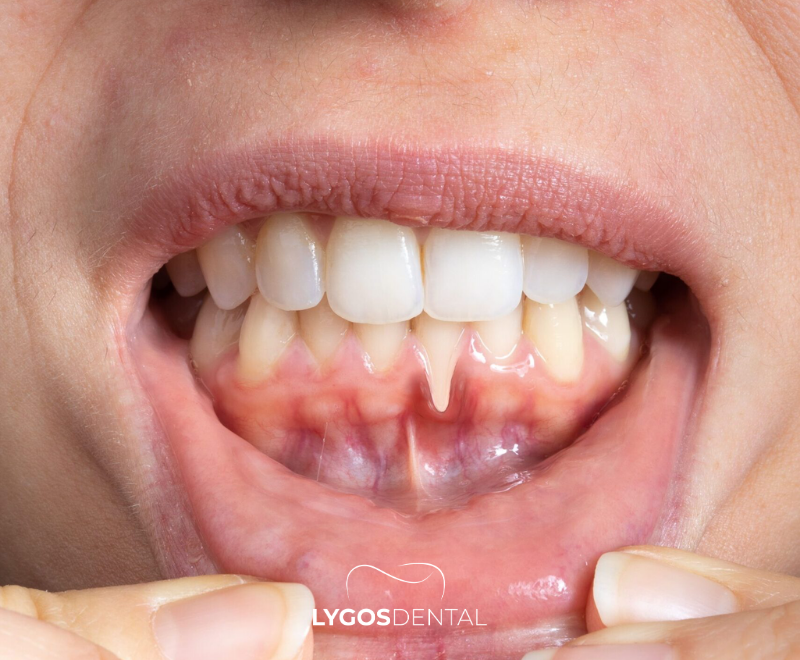
Chronic periodontitis is a slow-progressing but persistent gum disease characterized by inflammation of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It typically occurs in adults and often develops without noticeable symptoms for a long time. This disease is caused by bacterial infection resulting from the accumulation of plaque and tartar, eventually affecting the gum tissue, periodontal ligaments, and even the jawbone.
Common signs include gum recession, loose teeth, and bad breath. However, it may show no symptoms in the early stages, which allows it to progress silently.
Periodontitis is classified into two main categories: chronic and acute periodontitis. Although both cause inflammation of the gum and supporting tissues, there are key differences:
|
Feature
|
Chronic Periodontitis
|
Acute Periodontitis
|
|---|---|---|
|
Onset |
Slow and insidious |
Sudden and rapid |
|
Symptoms |
Mild to severe, often subtle |
Severe pain, swelling, sometimes fever |
|
Progression |
Develops over months or years |
Rapid progression in a short time |
|
Prevalence |
More common |
Less common |
|
Response to Treatment |
Requires regular maintenance |
Requires immediate intervention |
Chronic periodontitis is typically the primary form of gum disease, while the acute form usually results from trauma or a systemic condition.
The main cause of chronic periodontitis is bacterial plaque that accumulates on teeth. However, several factors contribute to its development:

While anyone can develop periodontitis, certain groups are more vulnerable. Risk factors include:
If you fall into any of these categories, you should take extra care of your gum health.
Chronic periodontitis usually progresses quietly, making early diagnosis critical. Symptoms include:
If you notice one or more of these signs, it’s important to see a dentist promptly.
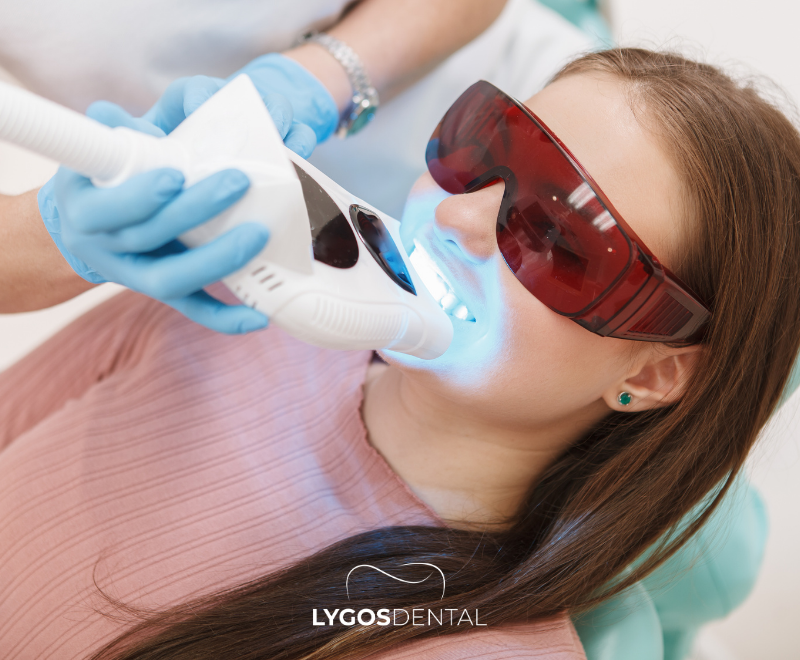

The primary goal in treating chronic periodontitis is to control infection and restore the health of the supporting structures. Treatment methods may include:
Chronic periodontitis can lead to tooth loss if not addressed but can be managed with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Maintaining oral hygiene, avoiding risk factors, and visiting the dentist regularly play key roles in prevention.
If you experience bleeding gums, swelling, or bad breath, consult a periodontist without delay. Remember, healthy teeth begin with healthy gums.
You can contact us here to learn more about Cosmetic Dentistry, Dental Crown, Dental Implant and General Dentistry to make an appointment and to get information about our services.
Chronic periodontitis is a progressive disease, so full recovery is not always possible. However, with early diagnosis and regular treatment, the disease can be halted, tooth loss prevented, and oral health significantly preserved. With consistent hygiene and checkups, recurrence can be avoided.
The duration depends on the severity. Mild cases may only need a few dental visits, while advanced cases may require months of treatment and follow-up. Surgical procedures may extend the healing process.
Yes. If left untreated, periodontitis can erode the bone supporting the teeth, causing them to become loose and eventually fall out. Prompt attention is essential upon noticing symptoms.
No. Periodontitis is not directly contagious. However, bacteria that cause the disease can be transmitted via saliva between partners or family members. Avoid sharing toothbrushes, and ensure everyone maintains good oral hygiene.

Special Note:
Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate

Special Note: Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate
Selenium Retro, Ataköy 7-8-9-10. Kısım, D-100 Güney Yanyolu No:18/A, 34158 Bakırköy/İstanbul
© 2025, LYGOS DENTAL. All Rights Reserved.