
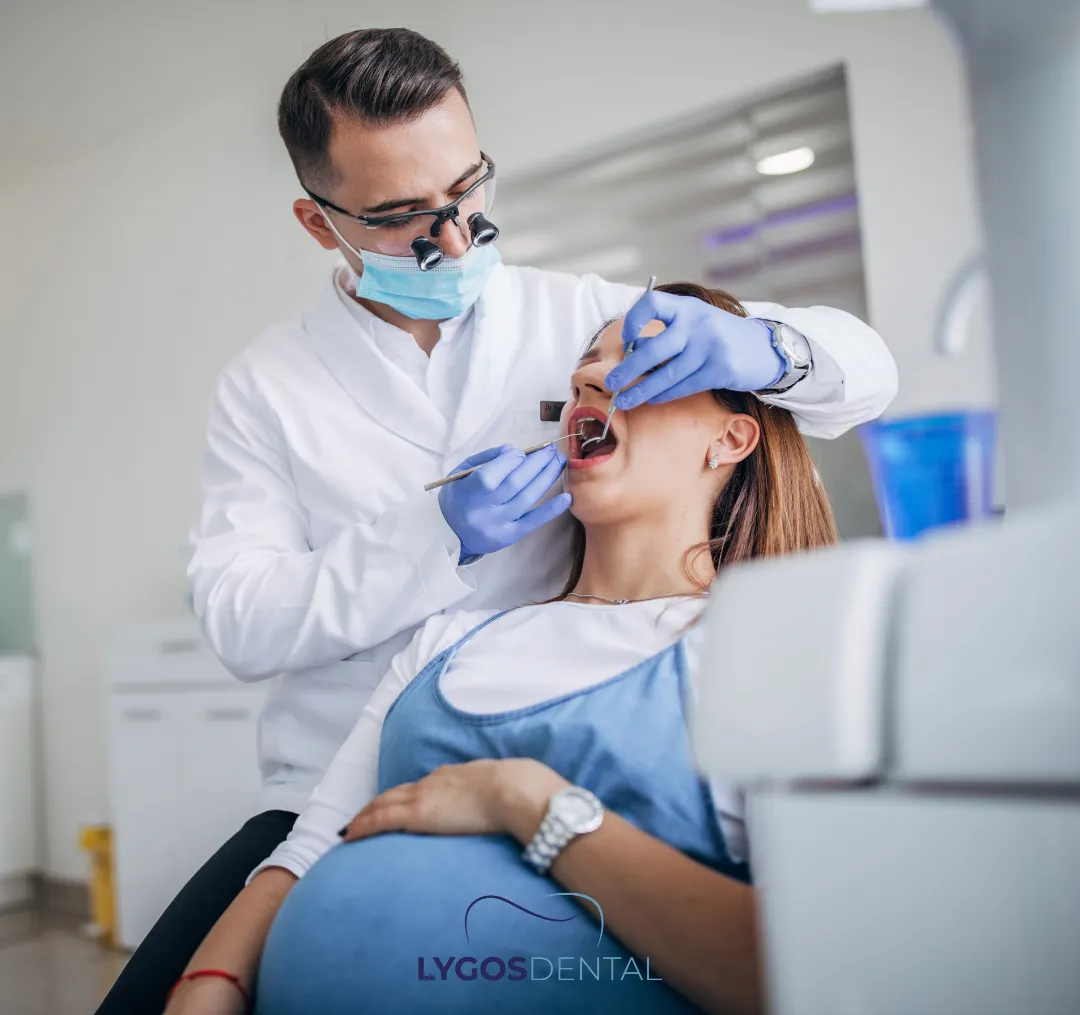
Dental implant procedures are technically possible during pregnancy. However, most dental and medical professionals strongly recommend against undergoing this procedure unless absolutely necessary. Dental implant surgery is an elective procedure involving multiple steps, such as surgery to insert a titanium post into the jawbone, follow-up visits, and additional dental work for placing the crown.
However, every stage of the procedure involves risks that are generally better to avoid while pregnant. One of the primary concerns is the use of dental X-rays, which are essential to evaluate the jawbone structure before and during the implant process. Although modern dental X-rays are safe and emit minimal radiation, any exposure to radiation during pregnancy even small amounts should be approached with caution.Moreover, the use of local anesthesia, antibiotics, and pain relievers required for the procedure could potentially harm the developing fetus. Stress is another consideration. While the dental implant procedure is routine and safe under normal circumstances, it can still cause physical and emotional stress, which may negatively impact pregnancy. For these reasons, dental implants are generally deferred until after childbirth.
This weakened immune state may increase the risk of infections after surgery, potentially leading to complications. Delaying dental implants allows the body to be in a better position to handle the procedure and recover more effectively. Lastly, pregnancy is a time to prioritize the baby’s development. Unnecessary medical interventions, such as elective surgeries, may introduce avoidable risks. By waiting until after childbirth, mothers can focus on their health and the health of their child without additional concerns.
If you are planning to undergo dental implant surgery, the ideal time to start the process is either before conception or after delivery. However, there may be circumstances where dental treatments cannot be delayed, such as addressing a damaged tooth or preventing an infection. Timing is an important factor in such situations.
Dental experts often recommend avoiding treatments during the first trimester. This recommendation stems from the fact that the first trimester is a vital phase of fetal development when key organs are forming. Any stress or exposure to medications during this phase could pose a higher risk to the baby. The second trimester, from weeks 13 to 26, is generally considered the safest window for necessary dental treatments.During this time, the baby’s development is more stable, and the mother may experience fewer symptoms like nausea and fatigue, making dental procedures more tolerable. However, even during the second trimester, elective surgeries like dental implants are discouraged unless deemed medically necessary. Additionally, the third trimester can pose physical challenges due to the growing abdomen, which may cause discomfort during dental procedures. Prolonged periods lying on the back might limit blood flow, leading to dizziness or unease. Stress or pain during procedures may also heighten the risk of premature labor. For these reasons, the third trimester is also not an ideal time for dental implants.
Brush your teeth at least twice daily using fluoride toothpaste and floss regularly to remove plaque buildup. These practices can help prevent gum disease and cavities, which are common during pregnancy.
Schedule routine dental checkups so your dentist can monitor your oral health and address any pregnancy-related issues promptly. Professional cleanings can also reduce the risk of gum inflammation.
A balanced diet that includes calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus supports both your overall health and the strength of your teeth and bones. Limit sugary snacks to reduce the chance of developing cavities.
If you experience increased gum sensitivity, a mild, alcohol-free mouthwash can soothe irritation and keep your mouth fresh.
If you intend to get dental implants after pregnancy, let your dentist know. They can offer tailored advice and ensure any existing oral health issues are addressed in the meantime.
However, many of these drugs are not considered safe for use during pregnancy, particularly in the first and third trimesters. Additionally, while dental X-rays used for implant planning are considered low-risk with modern equipment, avoiding any form of radiation exposure during pregnancy is a standard recommendation. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also interfere with tissue healing, a critical factor for the long-term success of the implant. For these reasons, waiting until after childbirth provides a safer environment for undergoing dental implant surgery.
You can contact us here to learn more about Cosmetic Dentistry, Dental Crown, Dental Implant and General Dentistry to make an appointment and to get information about our services.
Morning sickness, another common pregnancy symptom, can contribute to tooth decay. Vomiting-related stomach acid can erode enamel, heightening cavity risk. Rinsing with water or fluoride mouthwash after morning sickness episodes can help protect enamel. Pregnancy also tends to increase cravings and frequent snacking, which can elevate the risk of cavities. Maintaining a healthy diet and proper oral hygiene can counteract these effects.

Special Note:
Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate

Special Note: Our treatments are provided by healthcare facilities that possess a health tourism authorization certificate
Selenium Retro, Ataköy 7-8-9-10. Kısım, D-100 Güney Yanyolu No:18/A, 34158 Bakırköy/İstanbul
© 2025, LYGOS DENTAL. All Rights Reserved.